Analysis of Yohimbine and Analogs by UPLC/UV and by LC/MS/MS
resources - Recent Conference Materials
Analysis of Yohimbine and Analogs by UPLC/UV and by LC/MS/MS
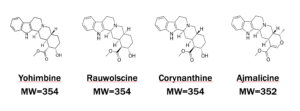
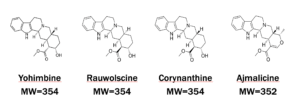
Yohimbine is extracted from the bark of a tree in central Africa. Rauwolscine, Corynanthine, and Ajmalicine are the major related alkaloid analogs. There are many other related alkaloid analogs as well.
Yohimbine has been studied as potential treatment for erectile dysfunction. Its use in dietary supplements is growing. It is used in traditional medicine. It reverses the effect of xylazine, a sedation drug used in animals.
ANALYTICAL CHALLENGES
Multitude of UPLC/UV peaks in sample extracts with similar absorption spectra require chromatographic separation. LC/MS/MS analysis still requires chromatographic separation because stereoisomers have same molecular weight. Wide variation in reported concentrations of these compounds by various laboratories.
Yohimbine Analogs Chemical Structures
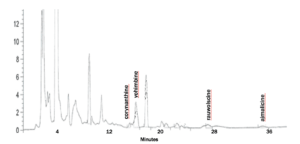
Outside Lab HPLC/UV Sample Extract
Genysis UPLC/UV Conditions
- Sample Prep: Dilute with 0.1 N HCl
- Linear Range: 2.0 – 20 ug/mL
- Column: Waters Cortecs C18 100 x 2 mm, 1.6 µm
- Mobile Phase A: 0.1% phosphoric acid in water
- Mobile Phase B: acetonitrile
- PDA: 219 (328 nm wavelength subtracted)
UPLC/UV SAMPLE EXTRACT
Genysis LC/MS/MS Conditions
- Sample Prep: Dilute with 1:1 MeOH:0.1%FA in water
- Linear Range: ~5 – 250 ng/mL (each analyte varies)
- Column: Waters Cortecs C18 100 x 2 mm, 2.7 µm
- Mobile Phase A: 0.1% formic acid in water
- Mobile Phase B: 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile
- MS Transitions used: 355→144 (yohimbine, rauwolscine, corynanthine), 353→144 (ajmalicine)
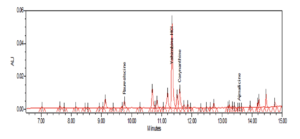
Analysis of 8% Yohimbine Extract (Raw Material)
CONCLUSION
Chromatographic separation between yohimbine and related alkaloid analogs is critical for accurate determination of concentrations. Without optimized separation, co-elution of related alkaloid analogs exists and reported concentrations may be biased high. UPLC/UV or LC/MS/MS can be adequately used for analysis. LC/MS/MS method has lower sensitivity.
